As of February 7, 2026, the intersection of aerospace engineering, artificial intelligence, and retail speculation has found a permanent home in prediction markets. With the recent, earth-shaking announcement of a merger between SpaceX and xAI on February 2, traders are no longer just betting on individual rocket launches; they are wagering on the formation of a $1.25 trillion "techno-conglomerate." Yet, while Elon Musk’s long-term visions carry a significant "Musk Premium" in valuation markets, a battle-hardened class of traders is making a fortune by betting against his immediate deadlines—a phenomenon now formally tracked as the "Elon Time" discount.
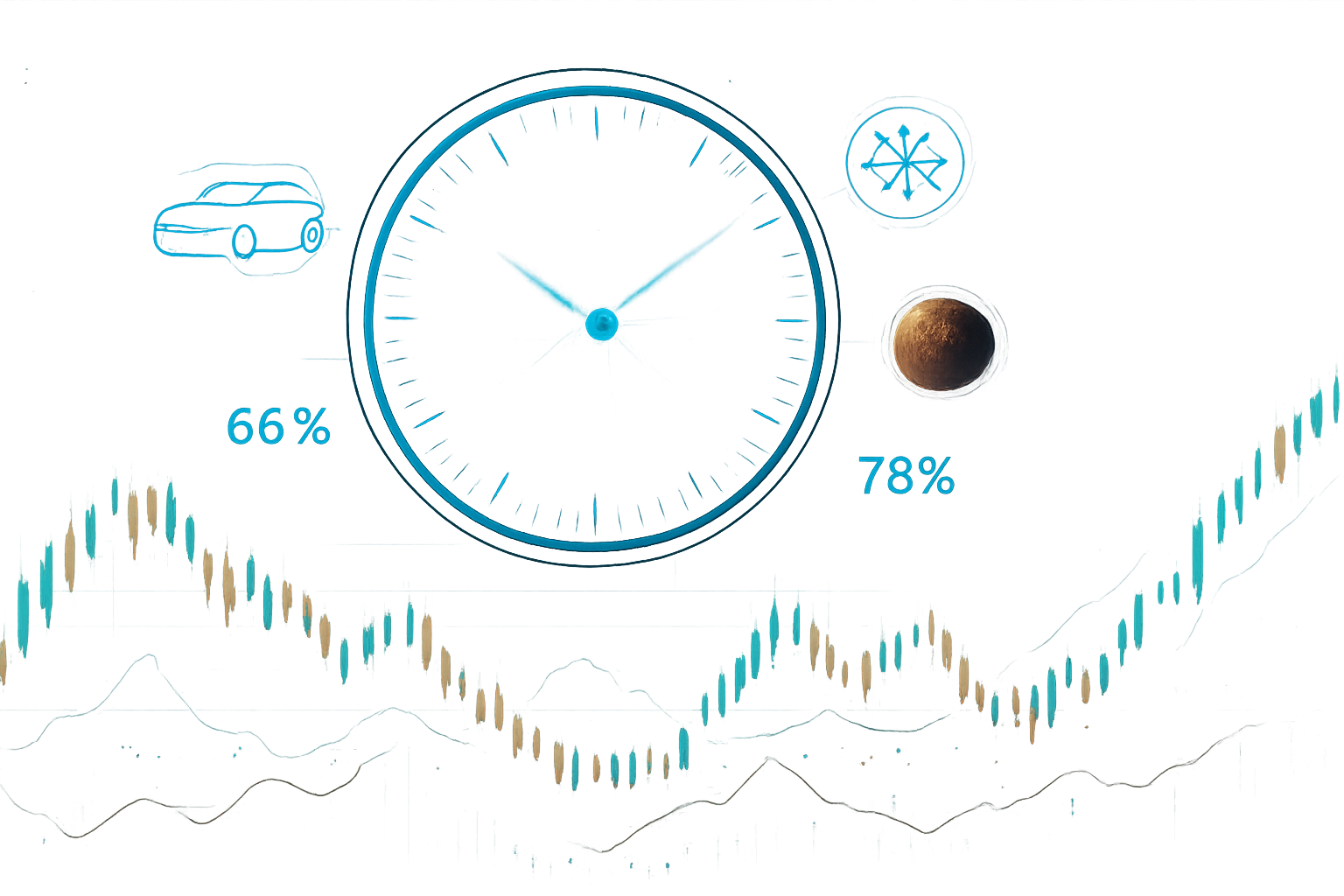
Currently, markets on Polymarket and Kalshi show a sharp divergence between belief and reality. While there is an 86% probability that SpaceX will achieve a valuation exceeding $1 trillion by the end of 2026, the odds of Musk meeting his self-imposed deadline for "Unsupervised" Full Self-Driving (FSD) by June have plummeted to 27%. This contrast highlights a growing sophistication among bettors: they believe in the man, but they don’t believe his calendar.
The Market: What’s Being Predicted
The "Musk Deadline" markets have become some of the most liquid contracts in the prediction market ecosystem. On Kalshi, a regulated U.S. exchange, and Polymarket, a decentralized global leader, three primary pillars of the "Musk-verse" dominate trading:
- SpaceX & Starship Milestones: Following the success of Flight 11 in late 2025, the market for Starship Flight Test 12 is currently at a 64% "Yes" for a successful landing or "catch" of the Super Heavy booster. Traders are also eyes-deep in the "2026 Mars Window" market. Despite Musk’s target of launching five uncrewed ships to Mars between November and December 2024, the market currently only gives a 7% chance to an intact landing on the Red Planet by year-end.
- Tesla (NASDAQ:TSLA) FSD and Robotaxis: Tesla markets have shifted from "When will FSD release?" to "When will the safety driver be removed?" Following a limited rollout of "Unsupervised FSD" in Austin late last year, the probability of a wider California launch by June 30, 2026, has dropped to 22%, as traders react to a slower-than-promised data ramp-up.
- The xAI-SpaceX Merger Synergy: A new "meta" market emerged this week regarding the SpaceX-xAI merger. Total Musk-related trading volume across all platforms exceeded $6.8 million in the first week of February alone, with millions more locked in speculative bets regarding the upcoming SpaceX IPO ticker (with $X currently leading at 64% odds).
Why Traders Are Betting
The driving force behind these markets is the "Elon Time" discount. Professional bettors have realized that Musk’s public statements often serve as "aspirational marketing" rather than "project management reality." Top traders on Polymarket have reportedly netted tens of thousands of dollars by consistently betting "No" on any Musk deadline that is less than six months away.
However, this skepticism is balanced by the "Musk Premium." Long-term contracts—those looking out two to five years—tend to be aggressively bullish. This reflects a belief that Musk eventually overcomes technical hurdles, even if he is perpetually "two weeks" late. For example, while traders are skeptical of a 2026 Mars landing, they are almost certain (88% odds) that SpaceX will go public by December 31, 2026, reflecting deep confidence in the company’s underlying commercial viability.
Recent news has further fueled this activity. The January announcement that Tesla would shift to a subscription-only FSD model by February 14, 2026, triggered a massive spike in volume for "FSD Revenue" prediction contracts. Whale activity has also been noted in "AGI by 2027" markets, which ticked up to 34% probability following the merger of Musk’s AI and aerospace interests.
Broader Context and Implications
The rise of Musk-deadline markets marks a shift in how the public consumes corporate news. Instead of relying on press releases or earnings calls from Tesla Inc. (NASDAQ:TSLA), many sophisticated observers now look to Kalshi and Polymarket as a more accurate "engineering truth." Prediction markets act as a real-time bullshit detector, aggregating the collective wisdom of thousands of engineers, data scientists, and industry insiders who "put their money where their mouth is."
This trend has significant real-world implications. Regulatory bodies like the CFTC and SEC are increasingly monitoring these markets to gauge public sentiment and potential insider movements. The historical accuracy of these markets has been remarkably high; in 2025, prediction markets accurately "called" the delay of the Starship Flight 10 booster catch three weeks before SpaceX officially announced the schedule shift.
Furthermore, these markets reveal a hardening of public sentiment. The "Musk Premium" suggests that while the billionaire’s brand may be polarizing, his perceived ability to execute on "impossible" engineering feats remains the bedrock of his companies' valuations.
What to Watch Next
The next 60 days will be a crucible for these markets. All eyes are on March 2026, the current target for Starship Flight 12. If the "Chopstick" arms of the launch tower successfully catch the Super Heavy booster again, we expect to see the "Mars 2026" landing odds double overnight, potentially jumping from 7% to 15-20%.
Another key milestone is the "4/20" Grok release. xAI is rumored to be preparing Grok 4.20, a meme-coded update aimed at showcasing the integrated compute power of the new "Colossus" supercomputer cluster. Markets currently price this release at a 97% certainty. However, the more technically significant Grok 5—which Musk claims has a 10% chance of achieving AGI—is viewed with more skepticism, with only a 12% probability of a Q1 2026 release.
Bottom Line
The Elon Musk prediction markets of 2026 have evolved into a sophisticated financial instrument that separates "vision" from "execution." The data is clear: traders believe in the eventual arrival of a $1.2 trillion Musk-led future, but they are unwilling to trust the billionaire’s calendar. The 2026 "Elon Time" discount remains a profitable strategy for those betting against short-term deadlines, even as long-term bullishness keeps SpaceX IPO odds at record highs.
Ultimately, these markets serve as a vital tool for price discovery in an era where corporate tweets can move billions of dollars. Whether it’s a rocket landing or a software update, the prediction market "tape" is proving to be a more reliable guide to the future than any social media post. As the SpaceX-xAI merger begins to take shape, the stakes—and the potential payouts—have never been higher.
This article is for informational purposes only and does not constitute financial or betting advice. Prediction market participation may be subject to legal restrictions in your jurisdiction.
PredictStreet focuses on covering the latest developments in prediction markets.
Visit the PredictStreet website at https://www.predictstreet.ai/.