In the world of retail finance, the "meme stock" era has officially been replaced by the "event contract" era. Leading this charge is Robinhood (NASDAQ: HOOD), which has successfully pivoted its massive user base from speculative equity trading toward the rapidly expanding frontier of prediction markets. As of early February 2026, the platform has moved far beyond its origins, transforming into a one-stop-shop where a user can buy Bitcoin, trade S&P 500 options, and now, hedge their weekend plans against an NFL upset—all within the same interface.
The timing could not be more critical. With Super Bowl LX between the Seattle Seahawks and the New England Patriots just days away, Robinhood’s prediction markets are seeing unprecedented liquidity. Unlike traditional sportsbooks that operate on a "house vs. player" model, Robinhood’s partnership with Kalshi allows users to trade directly against one another. This "peer-to-peer" (P2P) structure has driven the cumulative volume of event contracts on Robinhood to over 11 billion, creating a "truth engine" that many analysts believe is more accurate than any traditional polling or punditry.
The Market: What's Being Predicted
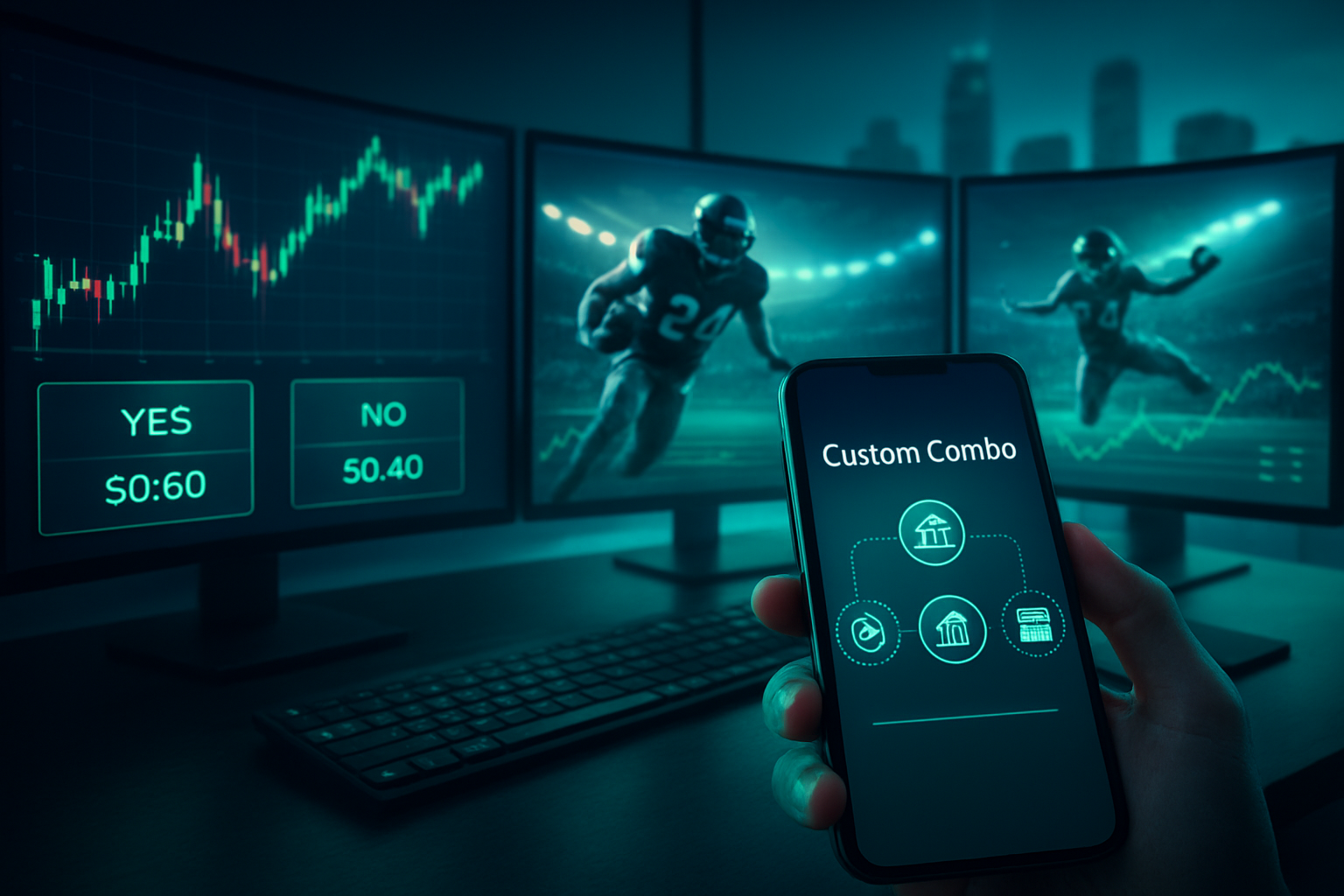
The current centerpiece of Robinhood's prediction ecosystem is its comprehensive suite of football event contracts, launched in partnership with the CFTC-regulated exchange Kalshi in August 2025. This market covers every NFL regular-season game and the "Power Four" college football conferences. Unlike the opaque odds of Las Vegas, these contracts trade between $0.00 and $1.00. If you buy a "Seattle Seahawks to Win" contract at $0.60, the market is effectively giving them a 60% chance of victory; if they win, your contract settles at $1.00, netting a $0.40 profit.
Since its inception, the platform has rapidly expanded its "menu" of outcomes. Traders can now speculate on point spreads, over/under totals, and as of December 2025, highly specific player props like anytime touchdowns or quarterback passing yards. The liquidity is staggering: the Super Bowl LX winner market alone has seen over $166 million in volume across the Robinhood-Kalshi ecosystem. This represents a nearly six-fold increase over the volume seen just one year ago, signaling a massive shift in how the public engages with major cultural events.
Why Traders Are Betting
The primary driver behind this retail migration is the introduction of "Custom Combos," a sophisticated feature that mimics traditional sports betting parlays but functions through a financial Request-for-Quote (RFQ) mechanism. When a user bundles up to 10 different outcomes—such as a Seahawks win, a Federal Reserve rate cut, and a specific movie’s opening weekend performance—Robinhood’s system polls market makers, led by Susquehanna International Group, to provide a real-time price.
Traders are also drawn to the efficiency of the "bid-ask spread" compared to the "vig" of a traditional sportsbook. While companies like DraftKings (NASDAQ: DKNG) or FanDuel typically bake a 5% to 10% margin into their odds, Robinhood's peer-to-peer model often sees spreads as thin as a single penny. "I'm not betting against a bookie who wants me to lose," says one high-volume trader on the platform. "I'm trading a financial instrument against someone who simply has a different view of the future."
Furthermore, the ability to "day trade" these contracts has revolutionized the experience. In a traditional bet, your money is locked until the final whistle. On Robinhood, if the Seahawks take a 14-point lead in the first quarter, the price of a "Yes" contract might jump from $0.60 to $0.85, allowing traders to exit early and lock in gains—a mechanic that feels much more like trading stocks than placing a wager.
Broader Context and Implications
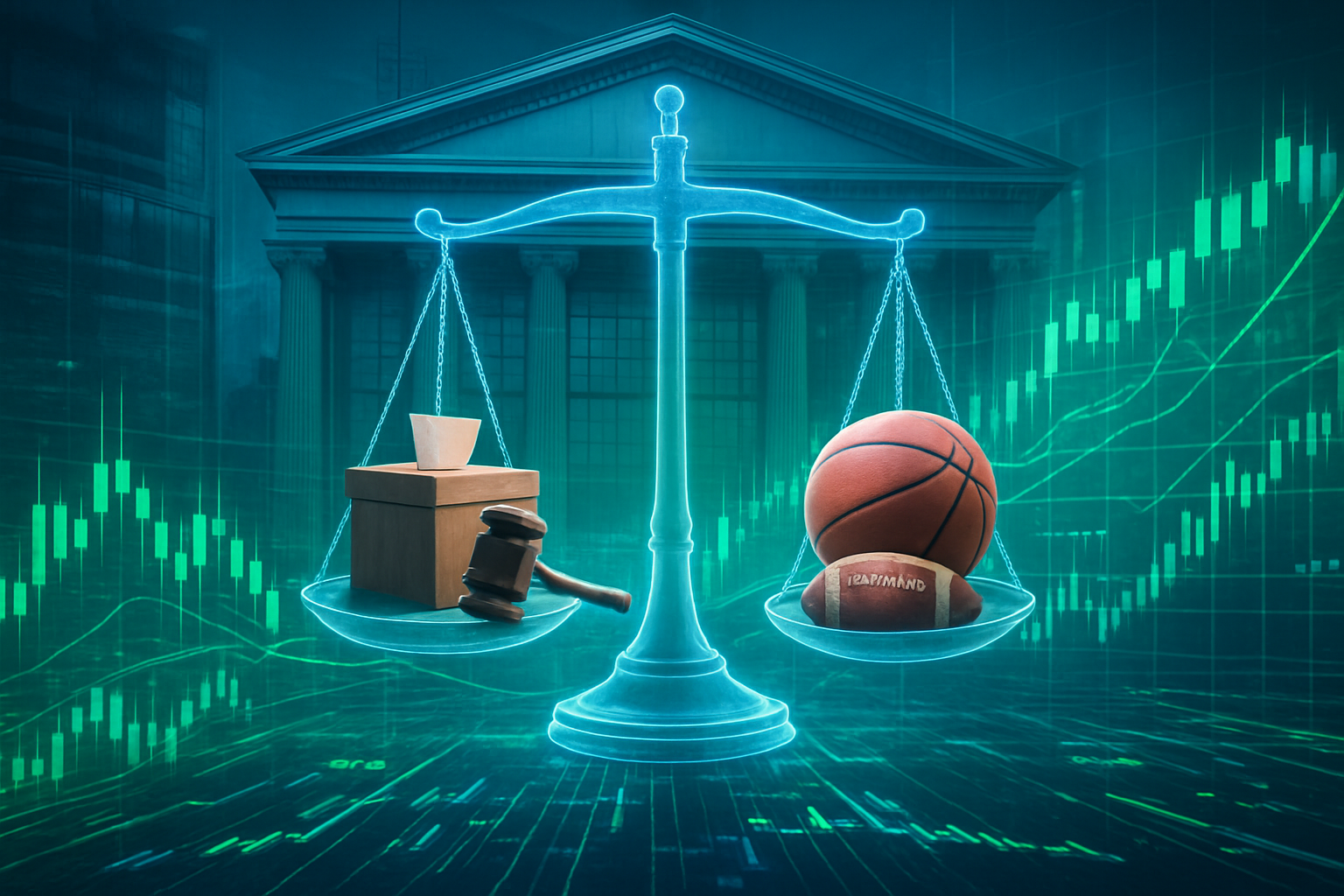
Robinhood’s aggressive expansion into this space is part of a larger strategic vision that CEO Vlad Tenev calls the "Prediction Market Supercycle." By framing these as "truth futures" rather than gambling, Robinhood is navigating a complex regulatory landscape. Because the trades are routed through the CFTC-regulated Kalshi—and soon through Robinhood's newly acquired MIAXdx (formerly LedgerX) exchange—the platform can offer these products in states where traditional sports betting remains illegal, such as California and Texas.
This vertical integration is a game-changer. In January 2026, Robinhood completed its 90% acquisition of MIAXdx, giving it its own Designated Contract Market (DCM) and clearinghouse. This move reduces the company's reliance on third-party partners and paves the way for "Robinhood-exclusive" contracts that could range from hyper-local weather events to corporate earnings outcomes.
The move is also paying off on the balance sheet. Prediction markets have become Robinhood’s fastest-growing revenue stream, currently on a trajectory to contribute over $300 million in annual revenue. It has effectively turned "news" into a tradable asset class, competing not just with sportsbooks, but with traditional derivatives exchanges like the CME Group (NASDAQ: CME) and Interactive Brokers (NASDAQ: IBKR), which has also launched its own "ForecastEx" platform.
What to Watch Next
As we move past the Super Bowl, the next major test for Robinhood’s infrastructure will be the 2026 mid-term election cycle and the integration of AI-assisted trading tools. Tenev has hinted at a future where users can use "AI Hedging Agents" to automatically buy event contracts that protect them against real-world risks, such as a rise in gas prices or a drop in their local housing market.
Additionally, the industry is closely watching for potential regulatory pushback. While the CFTC has currently allowed these "event contracts" to flourish, a shift in the political or legal winds could result in tighter restrictions on what qualifies as a "financial event." Robinhood’s ownership of MIAXdx is a defensive moat in this regard, providing it with the legal standing of a registered exchange rather than just a brokerage.
Bottom Line
Robinhood's pivot to prediction markets represents the final evolution of the "everything app" for the retail investor. By blurring the lines between sports, politics, and finance, the platform has created a high-engagement ecosystem that thrives on the 24-hour news cycle. The sheer volume seen in the 2025-2026 football season suggests that the public's appetite for "trading the truth" is only beginning to grow.
Ultimately, Robinhood (NASDAQ: HOOD) is betting that prediction markets will eventually be viewed as a core pillar of a modern portfolio. Whether it’s hedging a mortgage or speculating on a touchdown, the message to retail traders is clear: the future is no longer something to just watch—it’s something to trade.
This article is for informational purposes only and does not constitute financial or betting advice. Prediction market participation may be subject to legal restrictions in your jurisdiction.
PredictStreet focuses on covering the latest developments in prediction markets.
Visit the PredictStreet website at https://www.predictstreet.ai/.